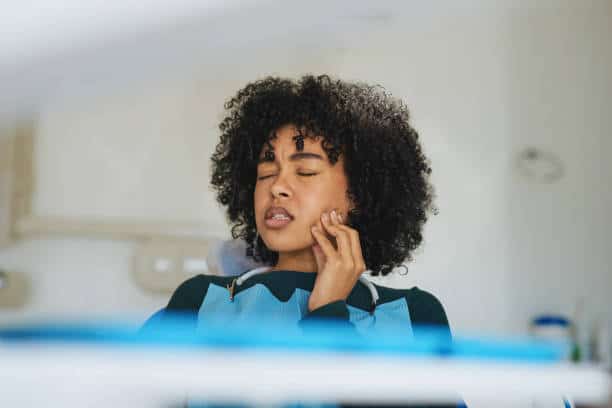

24 Jan How To Help Teeth Become Less Sensitive To Cold?
Your Tooth Doesn’t Have To Hurt

Tooth sensitivity to cold is a common dental concern that can cause discomfort and impact your quality of life. This condition occurs when the protective enamel on teeth becomes worn down or when gums recede, exposing the underlying dentin. Dentin contains microscopic tubules that connect to the nerves inside the tooth, making it more sensitive to temperature changes. Fortunately, there are several effective strategies to reduce cold sensitivity and improve your oral health.
Understanding the Causes of Cold Sensitivity
Before addressing tooth sensitivity, it’s essential to identify its root causes. Some common contributors include:
- Enamel Erosion: Caused by acidic foods, beverages, or aggressive brushing.
- Gum Recession: Often a result of gum disease or improper brushing techniques.
- Tooth Decay: Cavities can expose sensitive areas of the tooth.
- Teeth Grinding: Can wear down enamel over time.
- Dental Procedures: Whitening treatments or fillings may temporarily increase sensitivity.
- Cracked Teeth: These can expose the dentin or pulp, causing sharp sensitivity.
Improving Oral Hygiene Practices
Good oral hygiene is the foundation for reducing sensitivity. Implement these habits:
- Use a Soft-Bristled Toothbrush: This prevents enamel damage and gum recession.
- Brush Gently: Avoid aggressive scrubbing; use gentle, circular motions instead.
- Floss Daily: Removes plaque and debris that can contribute to gum recession.
- Use Fluoride Toothpaste: Strengthens enamel and reduces sensitivity.
Desensitizing Toothpaste
Desensitizing toothpaste is designed to alleviate sensitivity by blocking the pathways leading to the tooth’s nerves. Look for products containing potassium nitrate or stannous fluoride. For best results:
- Use it regularly, replacing your regular toothpaste.
- Apply a small amount directly to the sensitive area and leave it for a few minutes before rinsing.
- Combine with fluoride mouthwash for additional protection.
Avoid Acidic Foods and Drinks
Acidic substances can erode enamel and worsen sensitivity. Minimize or avoid:
- Citrus fruits and juices.
- Soda and carbonated beverages.
- Vinegar-based dressings.
- Wine and other acidic alcohols.
If you consume acidic foods or drinks, rinse your mouth with water afterward and wait at least 30 minutes before brushing to prevent further enamel erosion.
Wear a Mouthguard for Grinding
Teeth grinding, or bruxism, can wear down enamel and increase sensitivity. If you suspect grinding, especially during sleep, consult your dentist. They may recommend a custom-fitted mouthguard to protect your teeth.
Treat Gum Disease
Gum disease can lead to gum recession and expose sensitive tooth roots. If you notice signs like swollen or bleeding gums, seek professional treatment. Scaling and root planing (deep cleaning) can remove plaque and tartar buildup, helping gums reattach to teeth.
Professional Dental Treatments
For severe sensitivity, your dentist may suggest specific treatments, such as:
- Fluoride Treatments: Applied in-office to strengthen enamel.
- Dental Bonding: Covers exposed dentin with a resin material.
- Gum Grafts: Surgical procedures to cover exposed roots.
- Root Canal Therapy: For persistent sensitivity that doesn’t respond to other treatments.
Home Remedies and Natural Solutions
Some natural remedies may provide temporary relief for cold sensitivity:
- Saltwater Rinse: Mix ½ teaspoon of salt with a glass of warm water and rinse your mouth twice daily.
- Clove Oil: Apply a small amount to the sensitive area with a cotton swab.
- Green Tea: Known for its anti-inflammatory properties, it can be used as a mouthwash to strengthen teeth and reduce sensitivity.
Stay Consistent with Dental Visits
Regular dental checkups are essential for identifying and addressing the causes of underlying sensitivity. During these visits, your dentist can:
- Detect early signs of enamel erosion or gum recession.
- Provide professional cleanings to remove plaque and tartar.
- Offer personalized advice and treatments to manage sensitivity.
Adopt a Balanced Diet for Oral Health
A diet rich in essential nutrients supports healthy teeth and gums. Include:
- Calcium-Rich Foods: Milk, cheese, yogurt, and leafy greens strengthen enamel.
- Vitamin D: Promotes calcium absorption; found in fatty fish, eggs, and fortified foods.
- Phosphorus: Found in nuts, beans, and lean meats, it aids enamel repair.
- Antioxidants: Fruits and vegetables like berries, spinach, and carrots combat inflammation and gum disease.
Stay Hydrated
Dry mouth can exacerbate sensitivity by reducing saliva, which protects teeth. Drink plenty of water throughout the day and consider sugar-free gum to stimulate saliva production.
Avoid Extreme Temperature Changes
Sudden shifts from hot to cold can worsen sensitivity. Try to:
- Avoid consuming hot and cold foods or drinks together.
- Use a straw for cold beverages to limit contact with teeth.
- Warm cold foods slightly before consumption.
Conclusion
Reducing tooth sensitivity to cold involves a combination of good oral hygiene, dietary adjustments, and professional care. By addressing the underlying causes and adopting preventative measures, you can enjoy relief from discomfort and protect your teeth from further damage. Consistent dental visits are key to maintaining a healthy, pain-free smile. If sensitivity persists despite your efforts, consult a dental professional to explore advanced treatment options tailored to your needs.


Sorry, the comment form is closed at this time.